ADF provides ability to Drag and Drop items from one place to another place on the page. This simple tutorial will guide how to achieve this.
Requirements
- JDeveloper 11.1.2.2
- Oracle XE database with HR Schema in place.
Use Case
- Two tables are created on the page. Countries Table and Selected Countries Table.
- Rows are dragged from Countries table and dropped into Selected Countries Table
- Row should get added to the Selected Countries Table when dropped into it.
- Row should be deleted from source Countries table when successfully dropped into destination Selected Countries Table.
Setting up Business Components
First we will be creating a new table SELECTED_COUNTRIES which is exact replica of COUNTRIES table in HR Schema.
After this Create Entity object and View Object of both the tables(SELECTED_COUNTRIES and (COUNTRIES) and add these to AppModule.
From AppModule window -> Data Model Tab, shuttle the two newly created View Objects(SelectedCountriesView and CountriesView).
Below are the two VO which you can see. We have already shuttle them. (Please ignore “Rest of the VOs” in this screenshots and also in rest of screenshots in the post)
Creating JSF Page
Now create a new Jsf page in ViewController project. Lets give this page name – DragDropExample.jsf
Select One Column Footer (Stretched with Splitter) theme of the page as shown below.
Stretch the splitter to be in the middle of the page which divides the page in two halves.
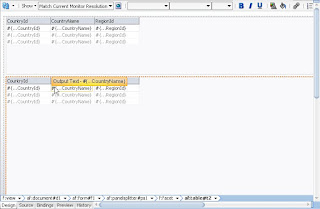
Now go to Data Control . Drag n Drop CountriesView1 to the first part of the page and create a read only table with single row selection.
Do the same thing with SelectedCountries data control on the second half of the page and create read only table with single row selection.
After this the page will look like below screenshot.
Adding ADF Drag – Drop components to our tables.
Now its the time to add drag and drop behavior to our tables so that we can drag from Countries table and drop in Selected Countries table.
From the Component Palette select the drag source and drag it under Countries table in structure window.
In the Drag Source Property Inspector give these values.
DragDropEndListener :- This is a method call to managed bean, which perform the tasks on the Source Collection after it has been dragged. For example , in our demo , we need to delete the row when it is being drag and dropped to the target SelectCountries table. So the code for deleting the row from the source collection goes into this method.
For this we need to create a new Managed Bean.
Lets create a new Bean by clicking arrow on DragDropEndListener field like below:
And create a new method named endListener and make EL of DragDropEndListener to
#{pageFlowScope.DragDropDemo.endListener}
We are all set on source side.
Now lets do the destination table side things.
From Component Palette selection Collection Drop Target. Drag this under SelectedCountries Table. This will pop up a window asking for the drop target. This again needs to be a method from managed bean. Make a new method named “dragRow” like below screenshot.
Below will be the values of Collection Drop Component in Property Inspector.
Model name needs to be same as Discriminant in drop source component. This is used in the dragRow method we will look below.Full Method name :- DragDropDemo.dragRow
And below is utility method addNewRow.
Full Method name :- DragDropDemo.addNewRow
And finally below is the code for DragDropEndListener method.
Full Method Name : DragDropDemo.endListener
Note that CountriesView1Iterator and SelectedCountriesView1Iterator used in the code are actual executable in DragDropExample.jsf. Below is screenshot for same.
Now we are all done. Do a Save all and compile everything and run the page DragDropExample.jsf.
You will see that you can drag n drop a row from Countries table to Selected Countries table. The row gets added on drop and gets deleted from the source table.
Hope this tutorial was helpful. Please feel free to ask any questions or doubts if you have any.
Happy Learning !!
Rohan Walia